Impulse Meaning in Physics
Impulse is a vector quantity direction is that of the force Unit. Not in Formula Booklet but important.
A sudden pushing force.

. Impulse is sometimes denoted by J. The motion produced by such a force. Web Impulse in physics - considerable force acting for a very short duration of time - impulse definition -example - formula - SI unit.
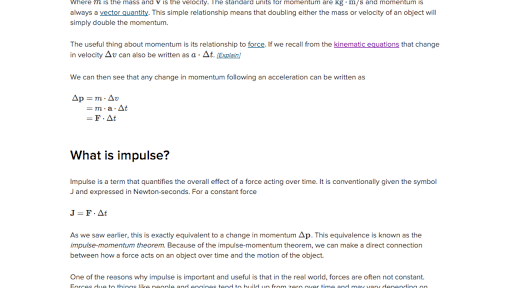
The equation really says that the. Mathematically impulse is equal ti change in momentum. Specific impulse is used to measure the efficiency of using specific fuels to generate thrust in such space vehicles.
It is usually represented by the symbol J and expressed in Newton seconds or. Impulse physics synonyms Impulse physics pronunciation Impulse physics translation English dictionary definition of Impulse physics. Dt shows it is with respect to time.
A sudden wish or urge that prompts an unpremeditated act or feeling. Web In fact thats the definition of impulse impulse equals the force applied multiplied by the time it was applied. Velocity is a vector.
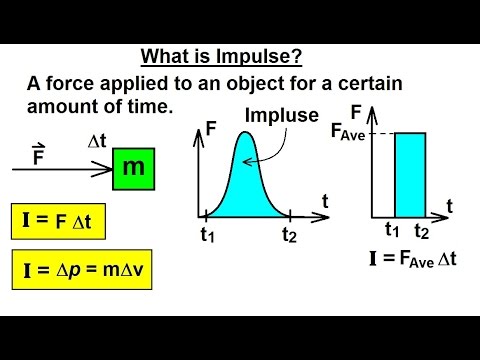
The same as momentum. Impulse Change in momentum. Web Impulse is a change in momentum.
During the collision an impulse is imparted by the wall to the molecule that is equal and opposite to the impulse imparted by the molecule to the wall. Web In words it could be said that the force times the time equals the mass times the change in velocity. The sum of the impulses imparted by all the molecules to the wall is.
Web Define Impulse physics. Impulse is also described as the change in momentum. Note that this is a vector equation because the force has a direction.
In momentum and impulse specific impulse is a quantification that is commonly applied in aerodynamic. In physics the quantity Force time is known as impulse. It is given to engines that generate thrust force.
Impulse is defined as the certain amount of force you apply at a given time interval. Cardiac impulse a heartbeat palpated over the left side of the chest at the apex of the heart. A sudden uncontrollable determination to act.
Impulse F t. Therefore the impulse does as well. Ns Newton-second Area under a force-time graph impulse.
1 Mechanical impulse is a measure of mechanical motion. This is required by Newtons third law. And since the quantity mv is the momentum the quantity mΔv must be the change in momentum.
Web Impulse physics In classical mechanics an impulse is defined as the integral of a force with respect to time. Web Impulse is defined as the product of force and time. Impulse can be an important quantity when youre solving physics problems because you.
It can be in electrical form - current or voltage or in force energy or acceleration. Web Impulse Definition and Formula The term pulse in physics has the purpose of describing or quantifying the effect of a force acting overtime on an object to alter its momentum. It is a vector quantity that for a mass particle is equal to the product of the mass m of the particle and its velocity v and has the same direction as the velocity vector.
See also point of maximal impulse. Web So in physics an impulse is any physical phenomena that has the time signature of an impulse. Web Specific Impulse Physics.
Momentum is defined as the cross product of mass and velocity. Good examples include rocket engines and jet engines. I is impulse sometimes marked J F is the force and.
Physics 9 5 Introduction To Momentum 6 Of 9 What Is Impulse Youtube
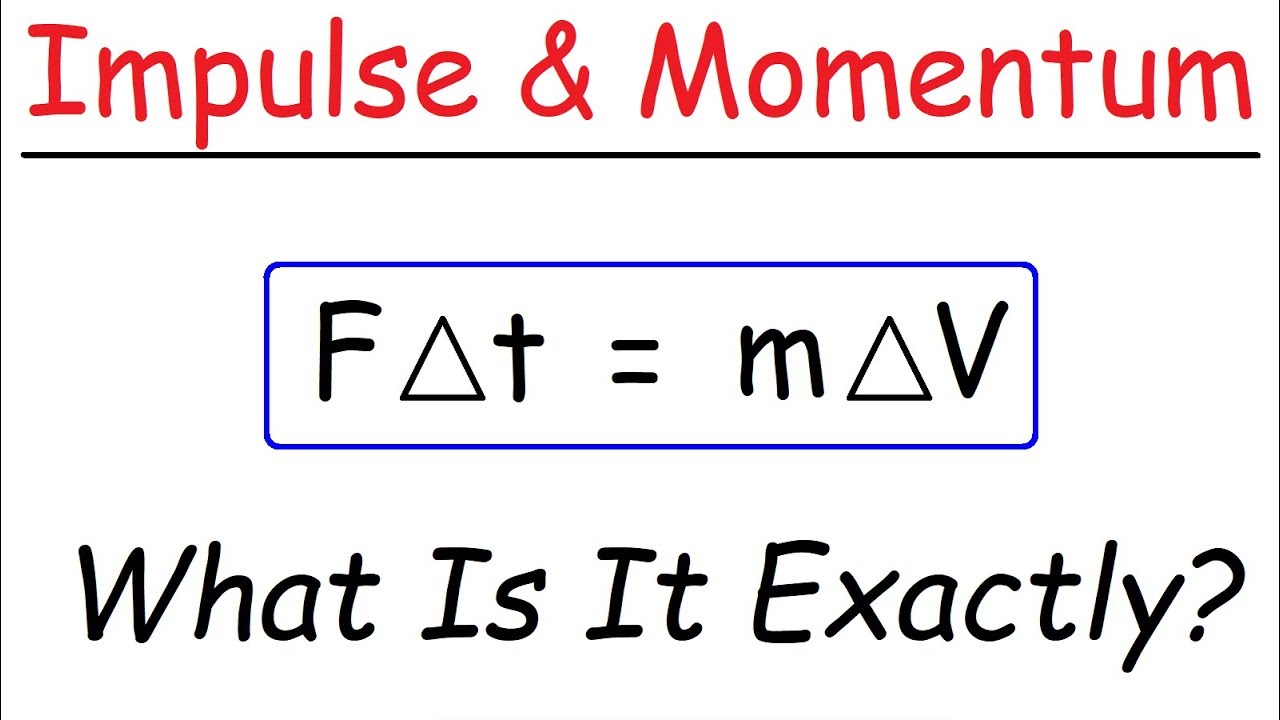
Introduction To Impulse Momentum Physics Youtube
What Are Momentum And Impulse Article Khan Academy

Impulse Units Definition Si Units Impulse Momentum Theorem Examples Real Life Scenario

Comments
Post a Comment